2025
Kilohertz volumetric imaging of in-vivo dynamics using squeezed light field microscopy
Zhaoqiang Wang*, Ruixuan Zhao*, Daniel A Wagenaar, Wenjun Kang, Calvin Lee, William Schmidt, Aryan Pammar, Enbo Zhu, Gerard CL Wong, Rongguang Liang, Tzung Hsiai, Liang Gao (* equal contribution)
Nature Methods 2025 Spotlight
We present squeezed light field microscopy (SLIM), a computational imaging method that enables rapid detection of high-resolution three-dimensional (3D) light signals using only a single, low-format camera sensor area. SLIM pushes the boundaries of 3D optical microscopy, achieving over one thousand volumes per second across a large field of view of 550 μm in diameter and 300 μm in depth. Using SLIM, we demonstrated blood cell velocimetry across the embryonic zebrafish brain and in a free-moving tail exhibiting high-frequency swinging motion.

2024
Hyperspectral retinal imaging in Alzheimer’s disease and age-related macular degeneration: a review
Xiaoxi Du*, Jongchan Park*, Ruixuan Zhao, R. Theodore Smith, Yosef Koronyo, Maya Koronyo-Hamaoui, Liang Gao (* equal contribution)
Acta Neuropathologica Communications 2024
In this review, we discuss recent advances in the field and outline the current bottlenecks and enabling technologies that could propel this field toward clinical translation.

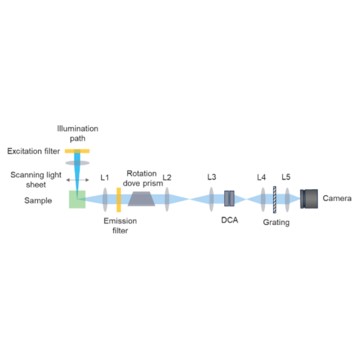
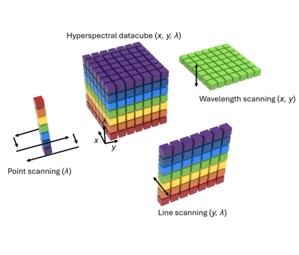
Cascaded spectral light field tomography
Qi Cui, Ruixuan Zhao, Zhaoqiang Wang, Liang Gao
Optics Letters 2024
We present cascaded spectral light field tomography for multicolor imaging in three dimensions (3D). Building upon light field tomography, our method uses a Dove prism array and a cylindrical lens array to transform a 3D scene into one-dimensional (1D) projections. To further enhance the reconstructed image quality, we incorporate a rotating Dove prism to increase the number of projection angles and a scanning light sheet to sparsify the sample along the depth axis. The resulting 1D projections are then spectrally dispersed for parallel spectral measurements. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our system in both fluorescence and scattering microscopy applications.

2023
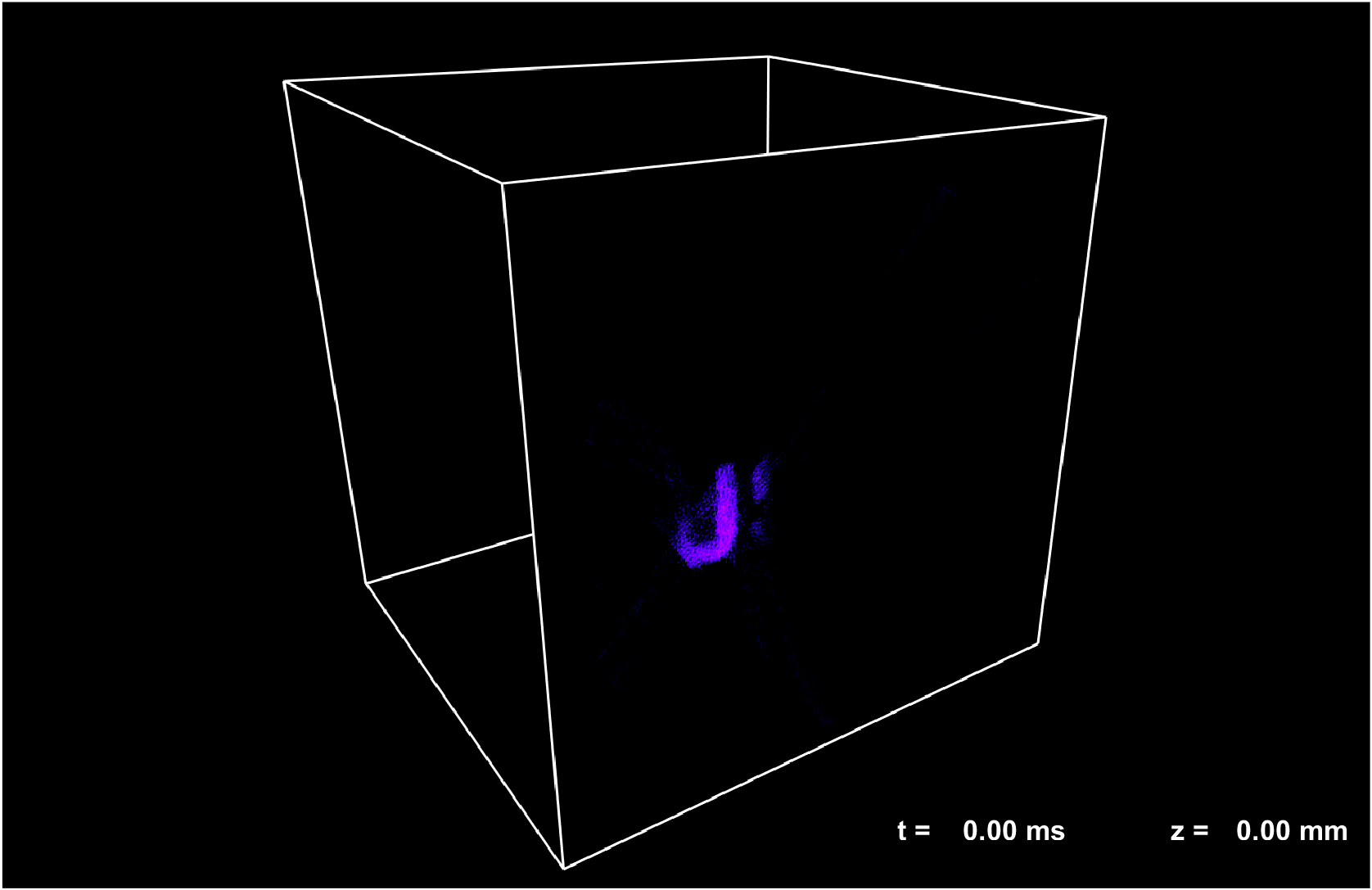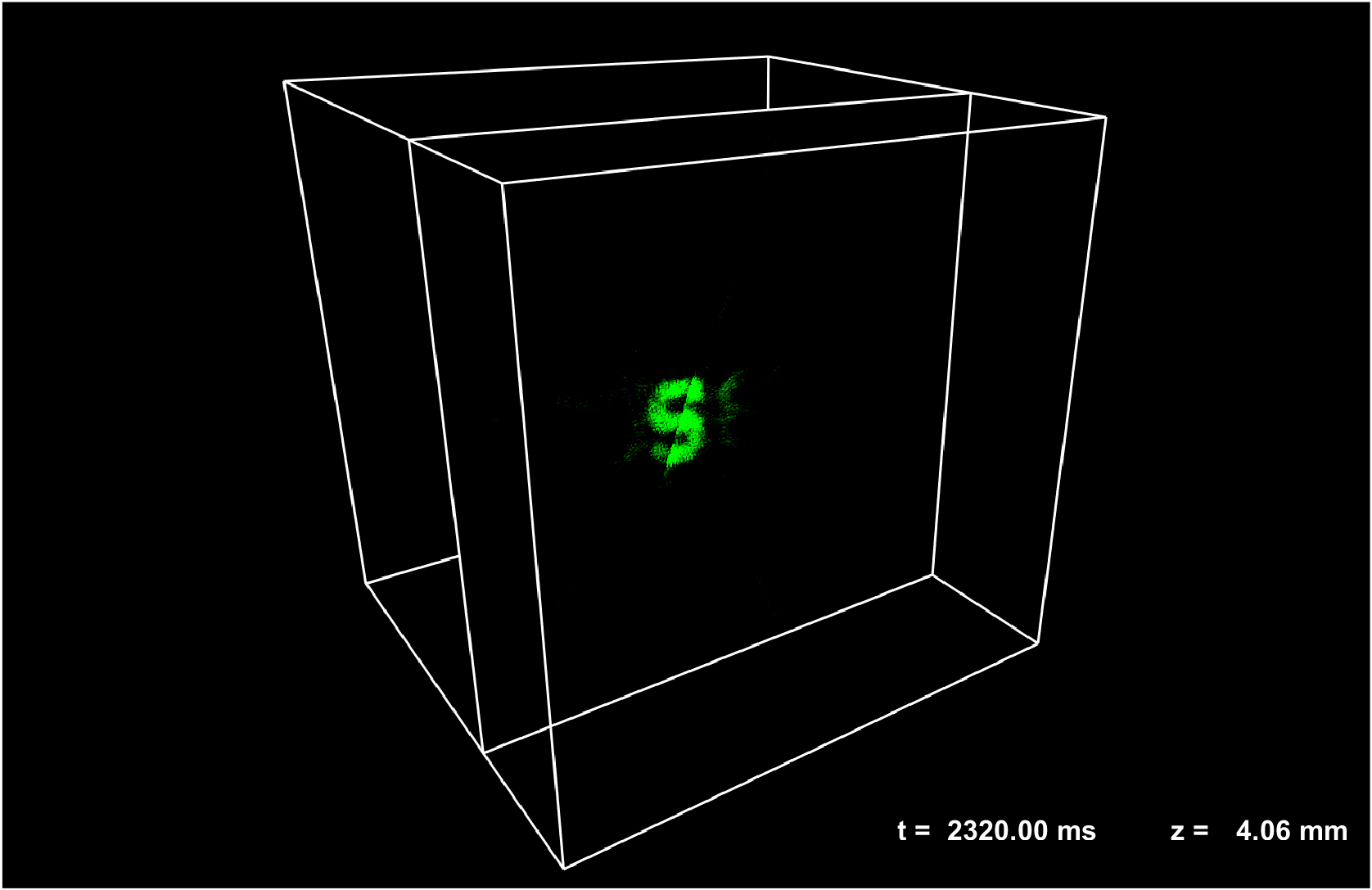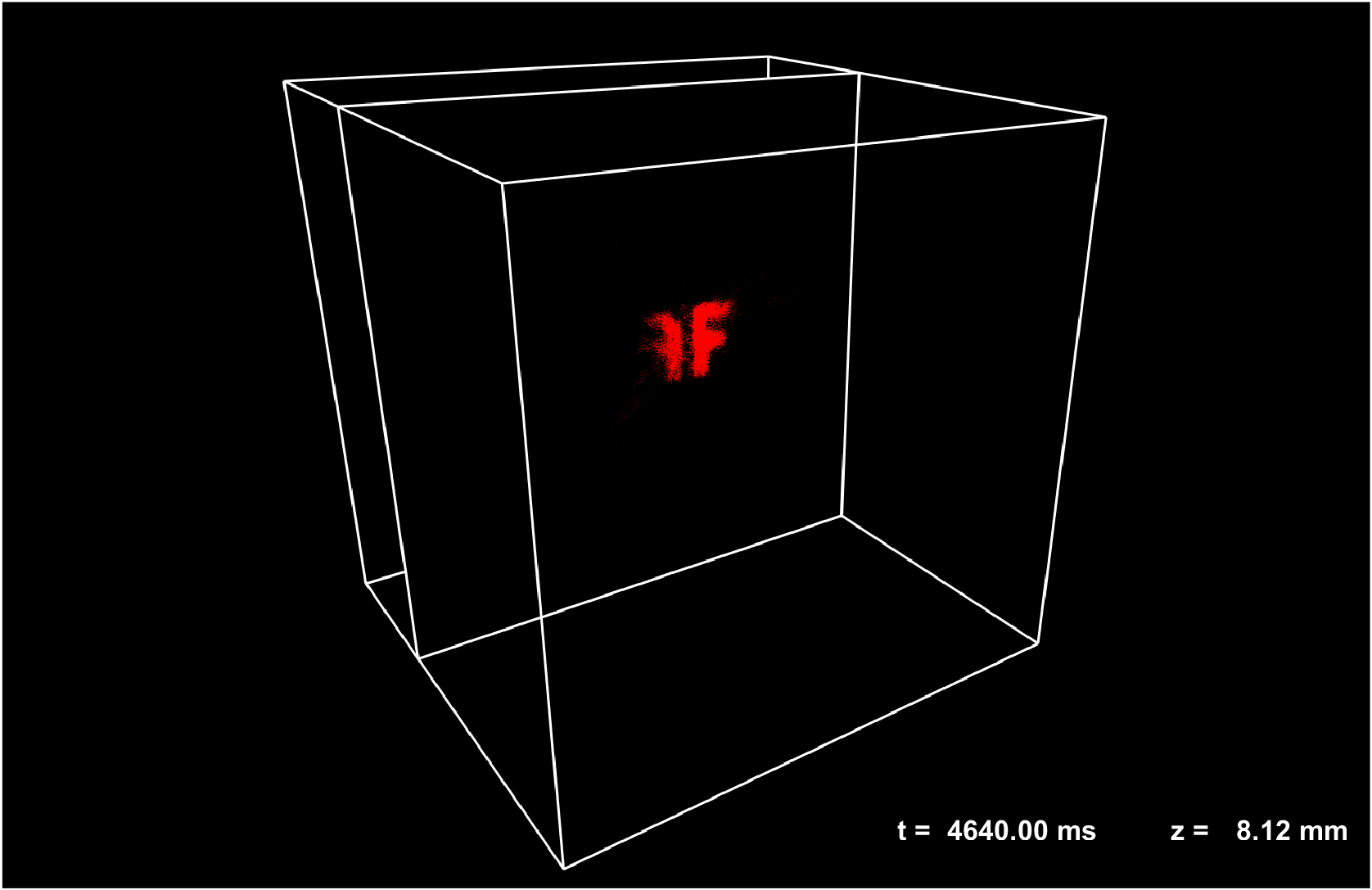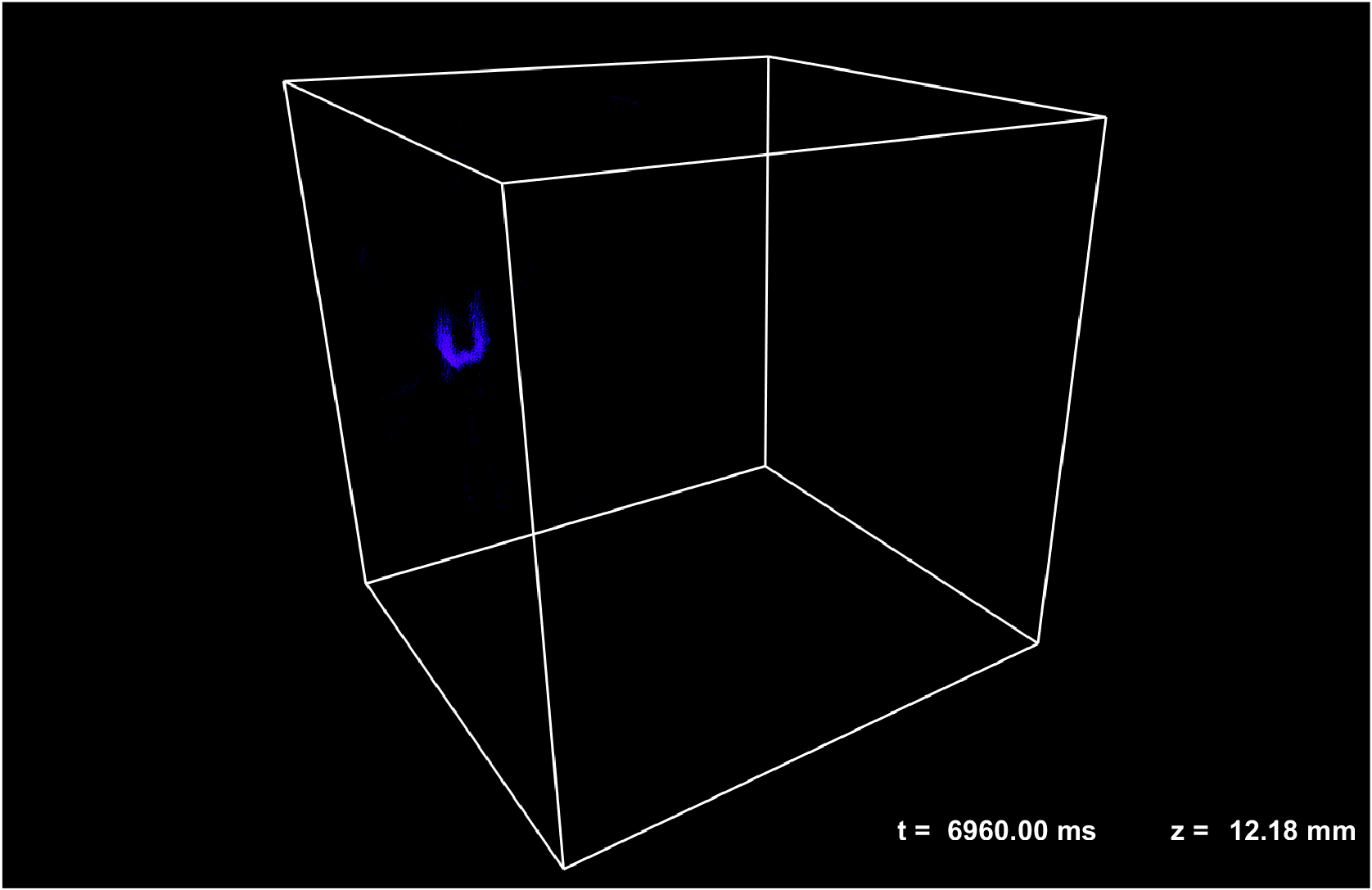
Coded aperture snapshot hyperspectral light field tomography
Ruixuan Zhao, Qi Cui, Zhaoqiang Wang, Liang Gao
Optics Express 2023 Editors Pick Optica Image of the week
We develope a novel two-stage cascaded compressed sensing scheme. By appropriately distributing the computation load to each stage, this method utilizes the compressibility of natural scenes in multiple domains, reducing the ill-posed nature of datacube recovery and achieving enhanced spatial resolution, suppressed aliasing artifacts, and improved spectral fidelity. Our approach efficiently records a five-dimensional (5D) plenoptic function in a single snapshot.

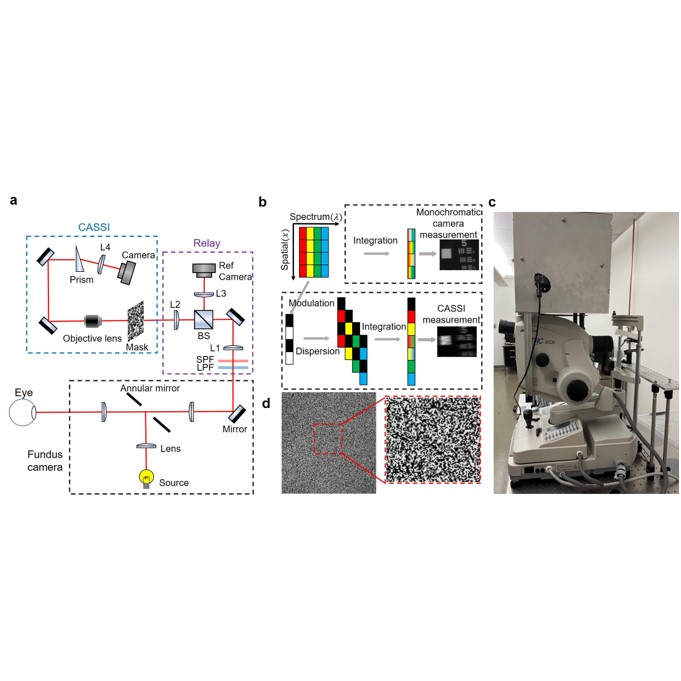
Coded aperture snapshot spectral imaging fundus camera
Ruixuan Zhao, Chengshuai Yang, R. Theodore Smith, Liang Gao
Scientific Reports 2023
We develope a prototype coded-aperture snapshot spectral imaging (HSI) fundus camera designed for clinical retinal imaging applications, incorporating a robust deep learning-based reconstruction method. The snapshot HSI fundus camera was demonstrated in in vivo retinal autofluorescence imaging of patients with age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Beyond its utility for AMD, HSI has also proven effective in identifying spectral biomarkers associated with other neurodegenerative conditions.

2019
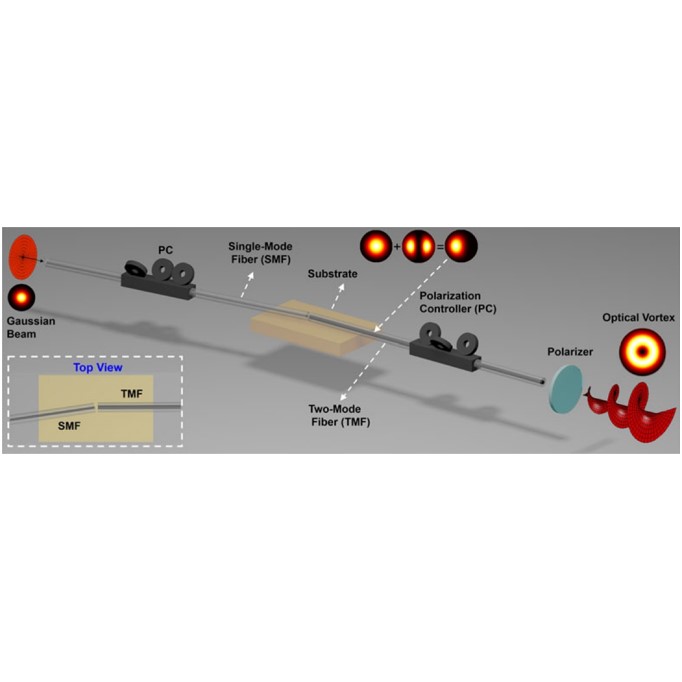
Generation of optical vortices using asymmetrically spliced fibers
Zhe Xu, Ruixuan Zhao, Shuhui Li, Li Shen, Cheng Du, Jian Wang
Journal of Optics 2019
We experimentally demonstrate a simple approach to generate optical vortex (OV) beams using optical fibers. The main structure is realized by asymmetrically splicing a standard simple-mode fiber with a two-mode fiber (TMF). The asymmetrical fusion joint can partly convert input fundamental mode to higher-order fiber modes. The unconverted fundamental mode component can be eventually filtered out through adjusting the states of two polarization controllers (PCs) applied on the two fibers and one polarizer located behind the output end of the TMF. By adjusting the two PCs, one can also selectively generate LP modes or OV modes with ℓ = ±1. The relationship between offsets and conversion efficiency is measured and analyzed, which accords well with the simulation. Mode purity and working bandwidth are also measured in the experiment.
